Open the equation editor dialog for the variable "effect price demand".
| Ø | Select the Equation edit tool. |
| Ø | Click on effect price demand. |
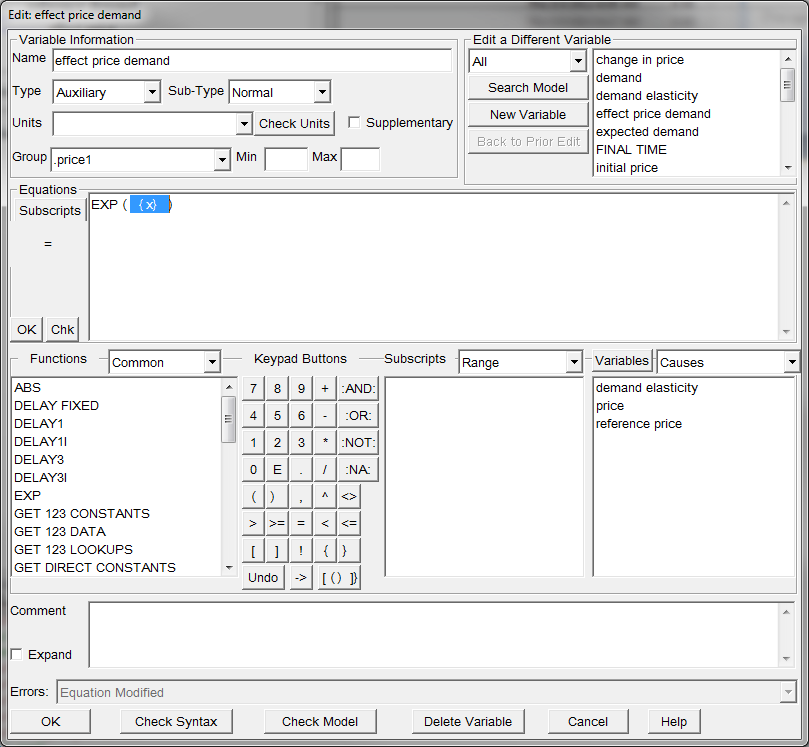
The "fx" button allows you to insert a function into the equation. Alternatively you can start typing "EXP" and Vensim will predict that you want to insert the EXP function.
In the editing window you should see EXP( {x} )
| Ø | Click on demand elasticity in the causes window. |
| Ø | Type LN or click the fx button and select the LN function. |
| Ø | You should now have something like EXP ( demand elasticity ) * LN ( {x} ) |
| Ø | Select the {x} text within the LN function. |
| Ø | Click on price in the causes window. |
| Ø | Press the / key or click on the / button. |
| Ø | Click on reference price in the variable list. |
Your equation should read:
| EXP(-demand elasticity*LN(price/reference price)) |

You can always type this in instead of working through the list of functions and sometimes this is easier to do.
A couple of notes on this equation are important. In this equation LN is the function for a natural logarithm and EXP(x) is the function that takes the special number e (about 2.72) to the power x. This equation could also be written as either one of:
| POWER(price/reference price,-demand elasticity*) |
| (price/reference price)^(-demand elasticity) |
(In fact, for this equation there are three additional formulas that involve switching price and reference price then changing the sign on demand elasticity.)
This equation is a standard constant elasticity demand curve. The use of price/reference price is a normalization that also prevents any units errors from occurring. We will discuss normalizations further in the next chapter.
Independent of which functions are used, the method for entering them is the same. You can either type them in, or select them from the list.

